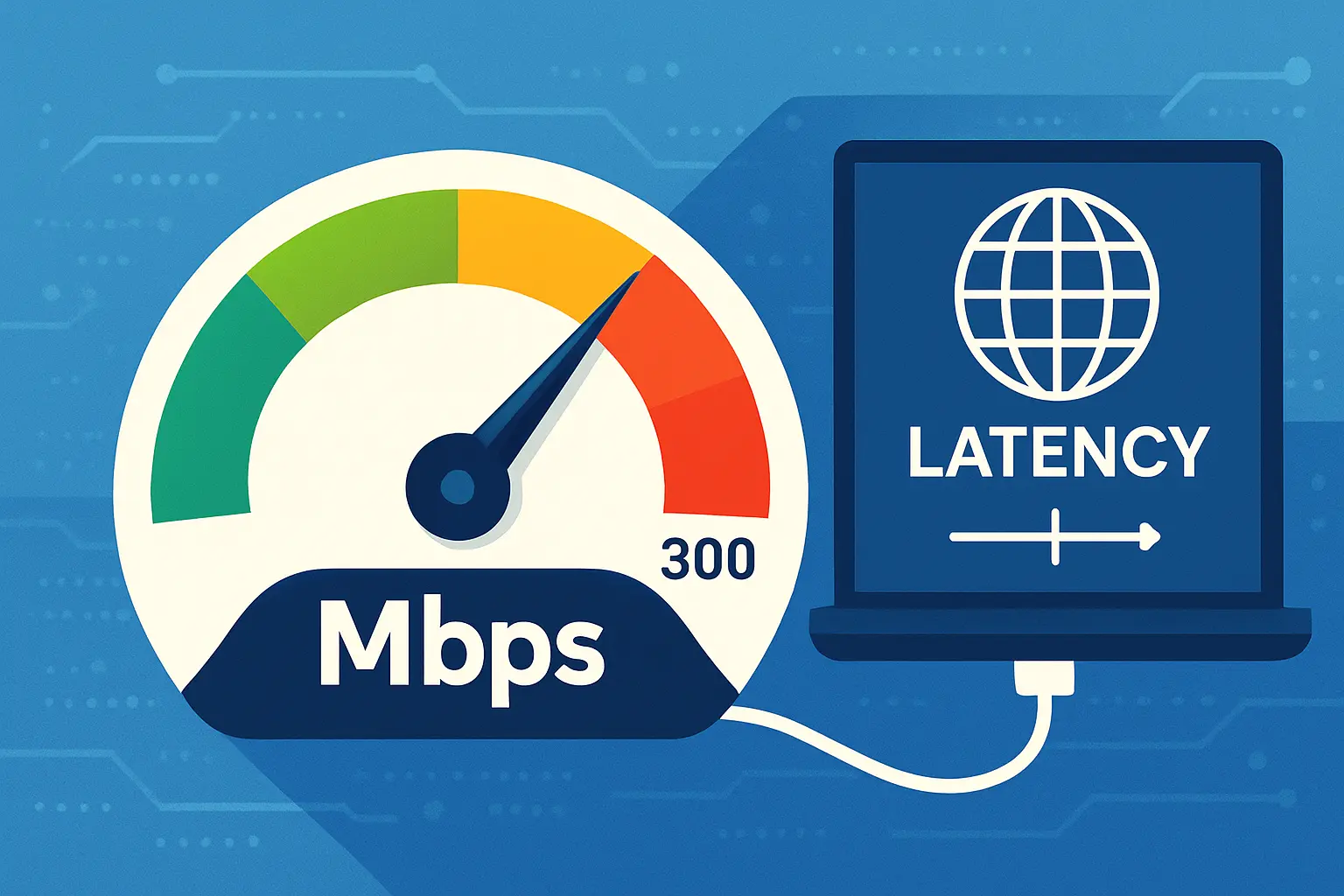
Understanding Internet Speeds: What Mbps and Latency Really Mean
When shopping for an internet plan or troubleshooting a slow connection, you’ll often come across terms like Mbps and latency. These metrics play a major role in your online experience — but what do they actually mean?
In this blog, we’ll break down the technical jargon into simple explanations. Whether you stream movies, games online, or work from home, understanding Mbps and latency can help you choose the right internet plan and make the most of your connection.
What is Mbps?
Mbps stands for Megabits per second, and it measures how fast data travels over your internet connection. One megabit equals one million bits of data. The more Mbps your internet connection has, the faster it can download or upload information.
Download vs Upload Speeds
- Download speed is how fast your connection can receive data. It affects activities like streaming, browsing, and downloading files.
- Upload speed is how fast your connection can send data. It’s important for video calls, uploading files, or hosting content.
For example:
- 25 Mbps download speed is suitable for basic streaming and browsing.
- 100+ Mbps is better for HD or 4K streaming, online gaming, and multiple devices.
Recommended Speeds by Activity
| Activity | Recommended Speed (Download) |
| Web browsing & email | 1-5 Mbps |
| HD video streaming | 5-10 Mbps |
| 4K video streaming | 25 Mbps or more |
| Online gaming | 3-6 Mbps |
| Video conferencing (Zoom, etc.) | 3-8 Mbps |
| Large file downloads | 50+ Mbps |
Keep in mind that these are per-device estimates. If multiple users are active simultaneously, you’ll need more bandwidth.
What is Latency?
Latency refers to the time it takes for data to travel from your device to the server and back — often measured in milliseconds (ms). You might hear latency referred to as ping in the context of gaming.
Why Latency Matters
High latency means there’s a delay in communication, which can cause:
- Lag in online games
- Delays in video calls or voice chats
- Slow response when loading websites
Low latency (under 50 ms) is ideal for real-time applications. High latency (over 100 ms) may still be acceptable for general browsing or streaming, but not for gaming or conferencing.
Examples of Latency Impact
- Gaming: A latency of 20-30 ms offers smooth gameplay. Over 100 ms can cause delays and lags.
- Video Calls: Low latency reduces awkward silences or overlapping conversations.
- Smart Home Devices: Faster response times improve device communication.
Mbps vs. Latency: Key Differences
| Metric | Measures | Unit | Affects |
| Mbps | Speed of data transfer | Megabits/sec | How fast data is downloaded or uploaded |
| Latency | Delay in data transmission | Milliseconds | How quickly data responds to actions |
While Mbps reflects the volume of data that can move in a second, latency reflects how quickly a single piece of data can travel. Think of Mbps as the size of a highway (more lanes = faster traffic), and latency as how quickly a single car gets to its destination.
Factors That Affect Both
1. Network Congestion
More users online at the same time can reduce available bandwidth and increase latency.
2. Router and Equipment Quality
Older routers or low-quality modems may limit your speed and cause lag.
3. WiFi Signal Strength
Weak or obstructed signals can reduce Mbps and increase latency, especially on 2.4 GHz networks.
4. Server Distance
If you’re accessing websites or games hosted on distant servers, latency naturally increases.
5. ISP Limitations
Your internet service provider may cap your bandwidth or throttle speeds during peak hours.
How to Check Your Internet Speed and Latency
Use tools like:
These tools will show:
- Download speed (Mbps)
- Upload speed (Mbps)
- Ping/latency (ms)
Tips to Improve Mbps and Latency
- Upgrade to a higher-speed internet plan.
- Use Ethernet cables instead of WiFi for critical devices.
- Move your router to a central location.
- Limit the number of connected devices.
- Restart your modem/router regularly.
- Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize important traffic.
Final Thoughts
Mbps and latency are two sides of the internet performance coin. Mbps affects how fast you can download or upload, while latency affects how responsive your connection feels. Together, they shape your experience — whether you’re streaming Netflix, competing in an online game, or attending a virtual meeting.
Understanding these metrics empowers you to choose the right plan and troubleshoot issues more effectively. If you’re still unsure whether your current speeds are meeting your needs, run a quick speed test — and if needed, talk to your internet service provider about upgrading or optimizing your setup.
Looking for a high-speed internet plan with low latency? Contact us today to find the best package for your home or business!